Jedsada Srijunpoe
Arduino Programming Problems
Problems 1)
- Write Arduino C/C++ programs that implement the following LED changing patterns (A, B, C, D).
- Use the Wokwi Simulator first to test your code and then verify the correctness using real hardware.
LED changing pattern: A
- Step 1. Initially, only one LED (at index=0) is ON, and the rest of the LEDs are OFF.
- Step 2. The position of the ON LED should be moved to the next in a circular manner in a fixed time interval and then repeat Step 2.
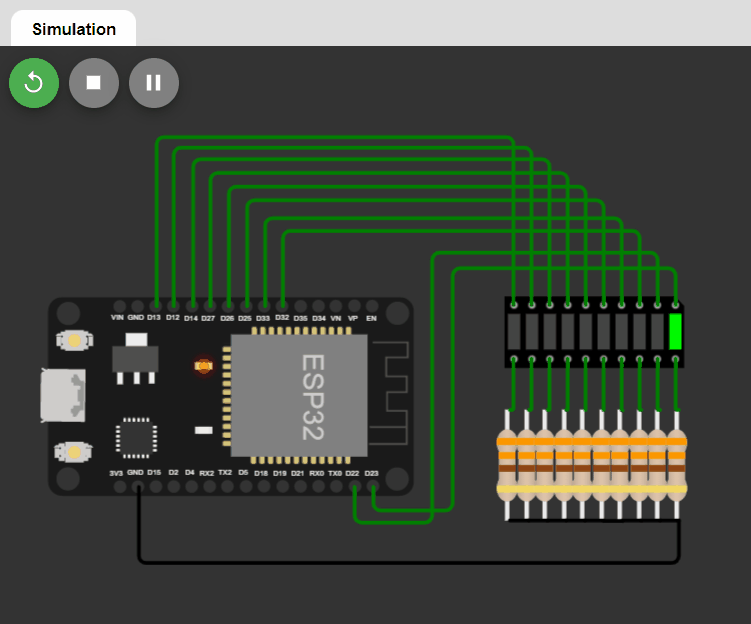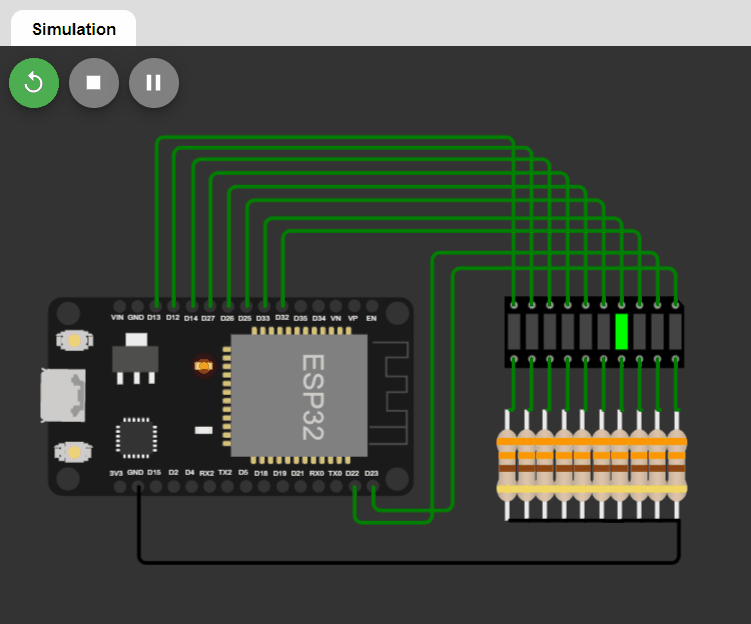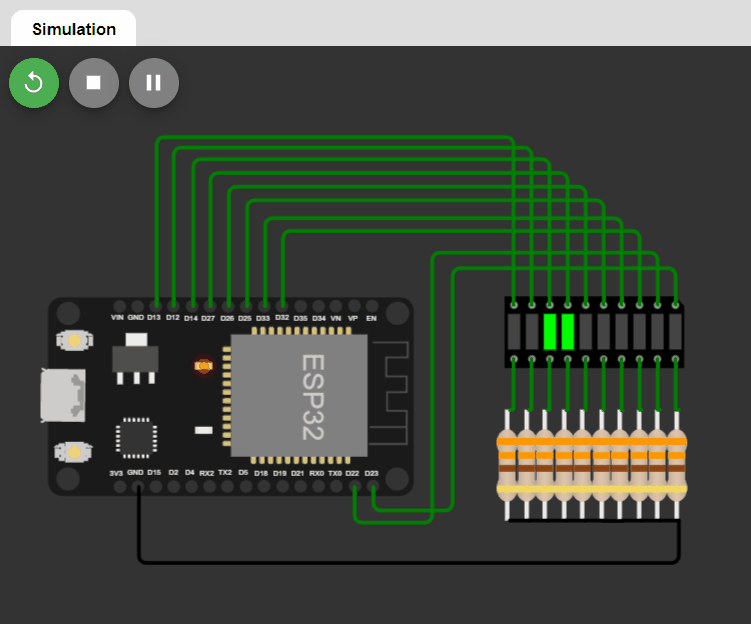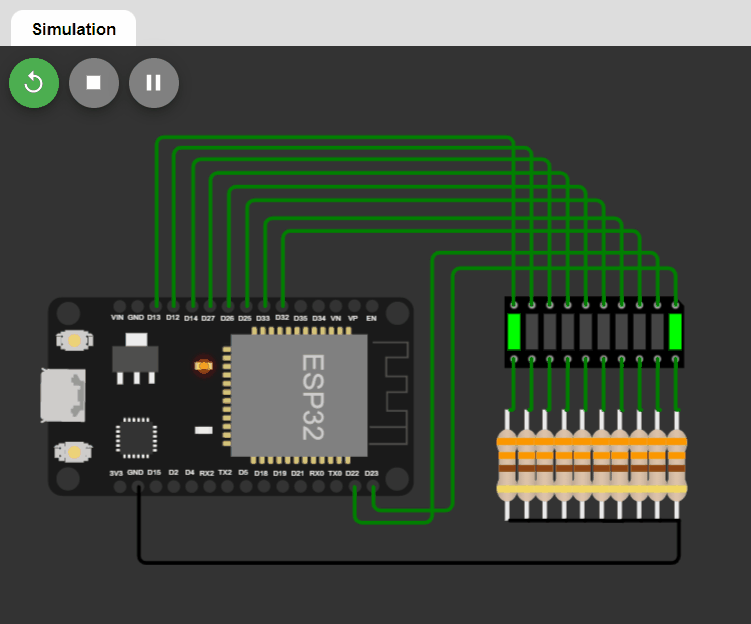
Code:
#if defined(ESP32)
const int LED_PINS[] = {23,22,32,33,25,26,27,14,12,13};
#else
const int LED_PINS[] = {2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11};
#endif
const int NUM_LEDS = sizeof(LED_PINS)/sizeof(int);
void setup() {
for ( int i=0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++ ) {
// set the direction of the i-th LED pin
pinMode( LED_PINS[i], OUTPUT );
// turn on the first LED (i=0) and the rest off.
digitalWrite( LED_PINS[i], (i==0) ? HIGH : LOW );
}
}
void loop() {
for ( int i=0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++) {
//turn on the i LED for 500 ms then turn off
digitalWrite( LED_PINS[i], HIGH);
delay(500);
digitalWrite( LED_PINS[i], LOW);
}
}
In this code, we have defined GPIO pins for Arduino Nano and ESP32 DevKit V1 by using LED_PINS array
If it’s ESP32 DevKit V1, we would use these pins
const int LED_PINS[] = {23,22,32,33,25,26,27,14,12,13};
If it’s Arduino Nano, we would use these pins
const int LED_PINS[] = {2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11};
I use ESP32 Devkit V1 for this pattern


Wokwi Simulator for this pattern: https://wokwi.com/projects/342300798050370131
LED changing pattern: B
- Step 1. Initially, all LEDs are OFF.
- Step 2. Turn on the LEDs one by one with a time delay, starting at index=0 until all LEDs are ON.
- Step 3. If all LEDs are ON, turn off LEDs one by one starting at index=n-1, where n is the total number of LEDs, until all LEDs are OFF, and repeat Steps 2-3.

Code:
#if defined(ESP32)
const int LED_PINS[] = {23,22,32,33,25,26,27,14,12,13};
#else
const int LED_PINS[] = {2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11};
#endif
const int NUM_LEDS = sizeof(LED_PINS)/sizeof(int);
void setup() {
for ( int i=0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++ ) {
// set the direction of the i-th LED pin
pinMode( LED_PINS[i], OUTPUT );
// turn on the first LED (i=0) and the rest off.
digitalWrite( LED_PINS[i], (i==0) ? HIGH : LOW );
}
}
void loop() {
for ( int i=0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++) {
// turn on the LEDs one by one with a time delay,
// starting at index=0 until all LEDs are ON.
digitalWrite( LED_PINS[i], HIGH);
delay(100);
}
for ( int j=0; j < NUM_LEDS; j++) {
// turn off the LEDs one by one starting at index=n-1,
// where n is the total number of LEDs, until all LEDs are OFF
digitalWrite(LED_PINS[NUM_LEDS-1-j], LOW);
delay(100);
}
}
In this pattern, I use Arduino Nano.


Wokwi Simulator for this pattern: https://wokwi.com/projects/342247407381119572
LED changing pattern: C
- Step 1. Initially, all LEDs are OFF.
- Step 2. Turn on the first LED by increasing the duty cycle of the PWM signal driving the LED, until the LED is fully ON.
- Step 3. Repeat Step 2 with the next LED until all LEDs are fully ON.
- Step 4. If all LEDs are ON, turn off LEDs one-by-one by decreasing the duty cycles of the PWM signals until all LEDs are OFF and repeat Steps 2-4.
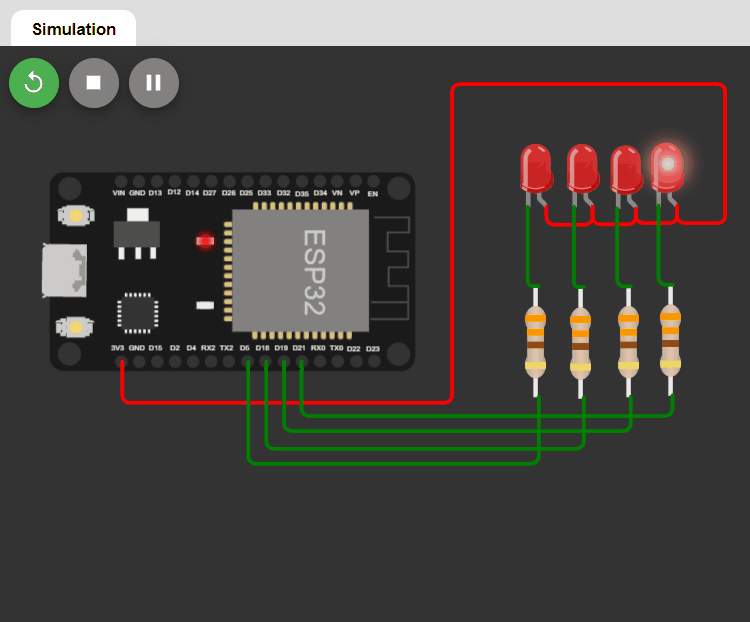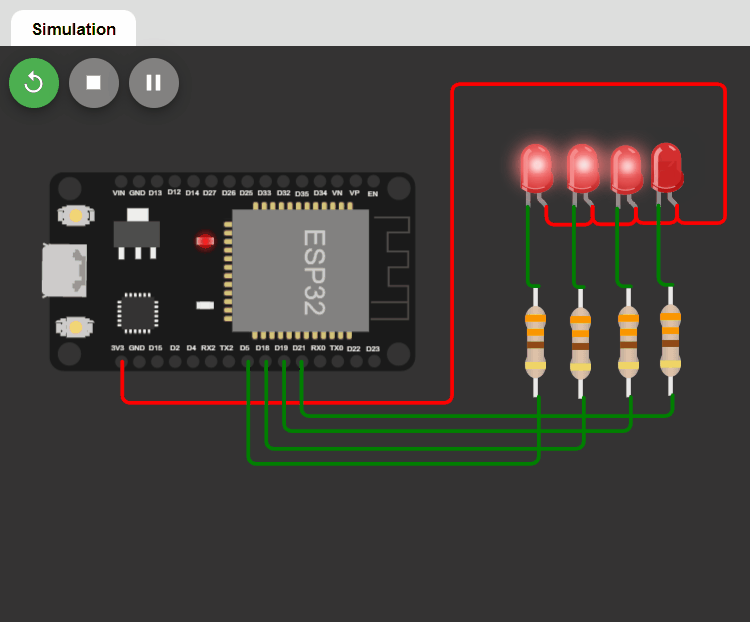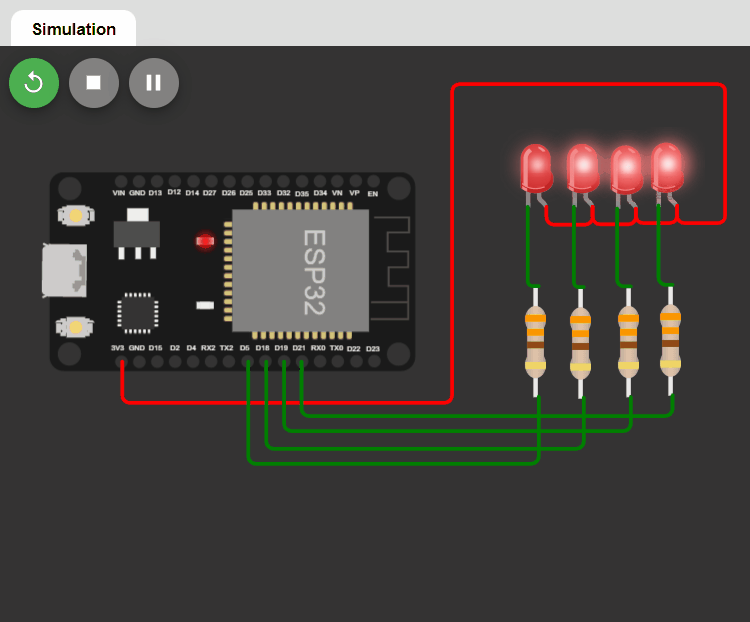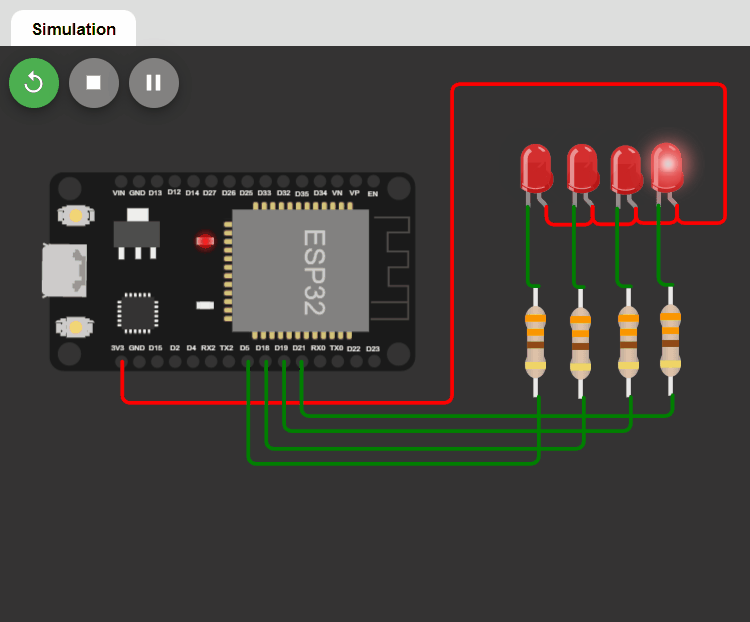
In this pattern, we need to use the duty cycle of the PWM signal.
We can control the duty cycle of the PWM signal by using LEDC API for ESP32.
Code:
const int LED_PINS[] = {5,18,19,21};
const int NUM_LEDS = sizeof(LED_PINS)/sizeof(int);
#define OFF (HIGH) // active-low LED
void setup() {
for ( int i=0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++ ) {
// set the direction of the i-th LED pin
pinMode( LED_PINS[i], OUTPUT );
digitalWrite( LED_PINS[i], OFF );
}
}
const int PWM_RESOLUTION = 8;
const int PWM_FREQ = 1000;
const int DUTY_MAX = (1 << PWM_RESOLUTION);
void loop() {
// turn on LEDs one by one by increasing the duty cycle of the PWM
for ( int i=0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++ ) {
ledcSetup( i /*channel*/, PWM_FREQ, PWM_RESOLUTION );
ledcAttachPin( LED_PINS[i] /*pin*/, i /*channel*/ );
for ( int x=0; x <= DUTY_MAX; x++ ) {
ledcWrite( i, DUTY_MAX-x );
delay(1);
}
}
// turn off LEDs one by one by decreasing the duty cycle of the PWM
for ( int i=0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++ ) {
ledcSetup( i /*channel*/, PWM_FREQ, PWM_RESOLUTION );
ledcAttachPin( LED_PINS[i] /*pin*/, i /*channel*/ );
for ( int x=0; x <= DUTY_MAX; x++ ) {
ledcWrite( i, x );
delay(1);
}
ledcDetachPin( LED_PINS[i] );
digitalWrite( LED_PINS[i], OFF );
}
}


Wokwi Simulator for this pattern: https://wokwi.com/projects/342312038793478740
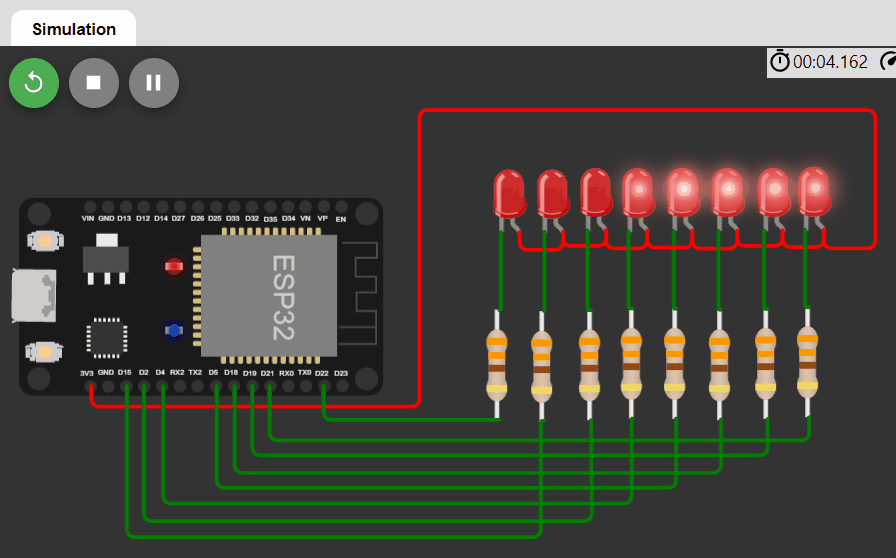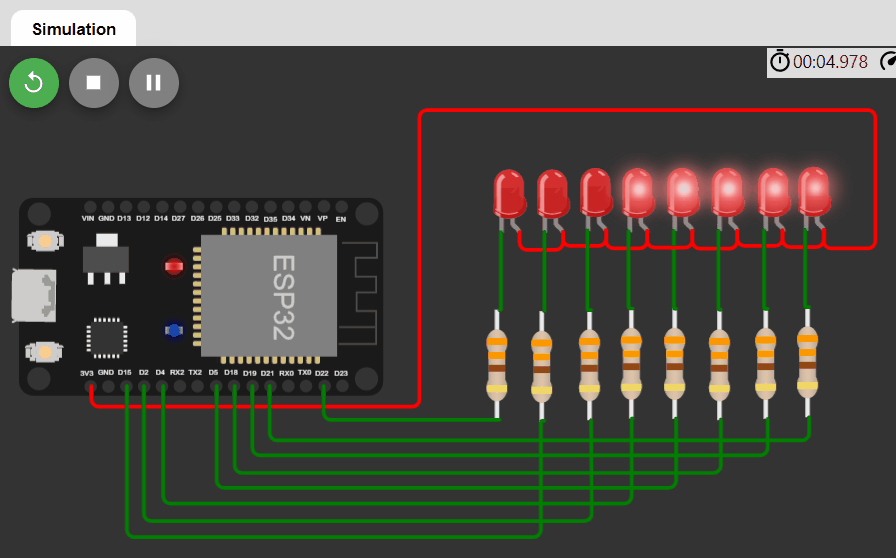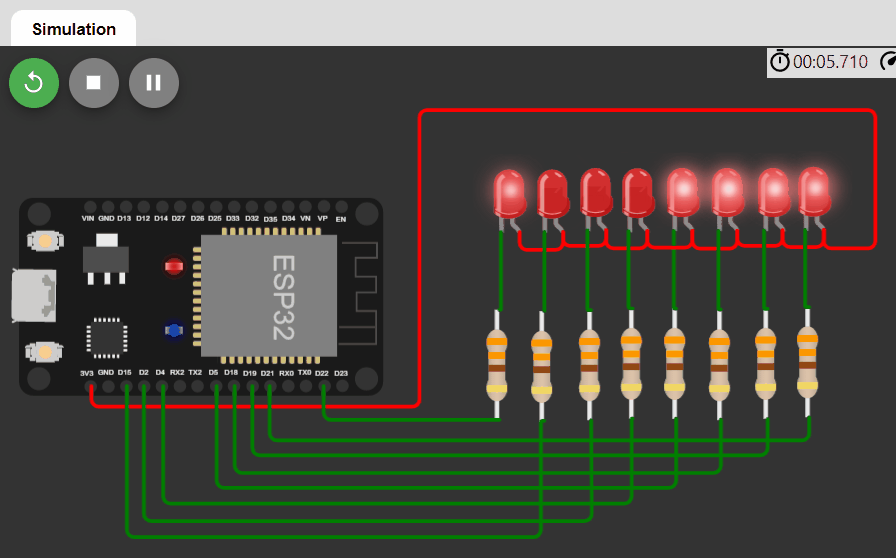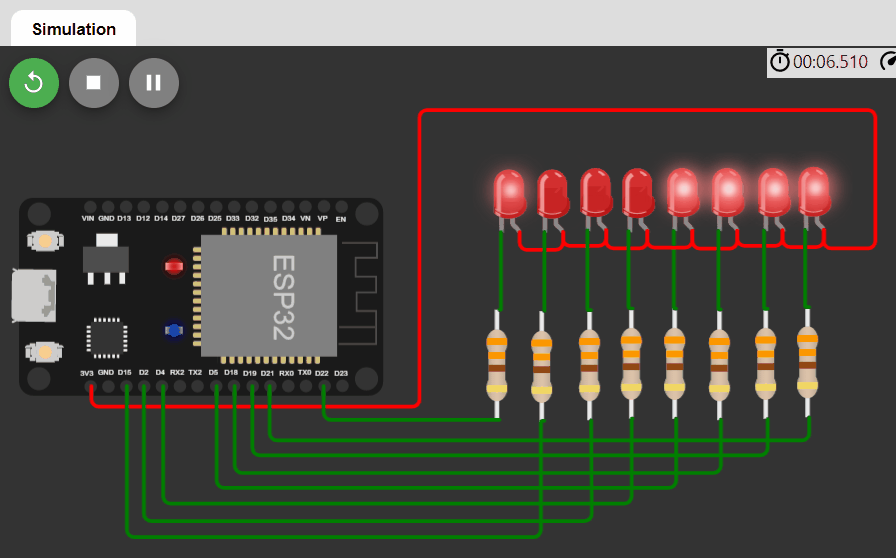
LED changing pattern: D
- Step 1. Initially, all LEDs are OFF.
- Step 2. Turn on the first 4 LEDs using PWM signals, each with different duty cycles (e.g. 100%, 50%, 25%, 10%), and the rest of the LEDs are OFF.
- Step 3. Move the positions of ON LEDs to the left by one position in a circular manner and repeat Step 3.
Code:
const int LED_PINS[] = {21, 19, 18, 5, 4, 2, 15, 22};
const int NUM_LEDS = sizeof(LED_PINS) / sizeof(int);
#define OFF (HIGH) // active-low LED
void setup() {
for ( int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++ ) {
// set the direction of the i-th LED pin
pinMode( LED_PINS[i], OUTPUT );
digitalWrite( LED_PINS[i], OFF );
}
}
const int PWM_RESOLUTION = 8;
const int PWM_FREQ = 1000;
const int DUTY_MAX = (1 << PWM_RESOLUTION);
// duty cycles 10%, 25%, 50%, 100%
const float DUTY_CYCLES[] = {0.1,0.25,0.5,1};
void loop() {
// starting at index=0, and move the positions of ON LEDs to the left by one
for ( int i=0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++) {
// turn on 4 LEDs, each with different duty cycles
for ( int j=0; j < 4; j++) {
ledcSetup( j, PWM_FREQ, PWM_RESOLUTION );
ledcAttachPin( LED_PINS[(i+j)%NUM_LEDS], j );
ledcWrite( j, (1 - DUTY_CYCLES[j])*DUTY_MAX );
}
delay(100);
// turn off the 4 LEDs
for ( int j=0; j < 4; j++) {
ledcDetachPin( LED_PINS[(i+j)%NUM_LEDS] );
digitalWrite( LED_PINS[(i+j)%NUM_LEDS], OFF );
}
}
}


Wokwi Simulator for this pattern: https://wokwi.com/projects/343517173322351187
Problems 2)
Reimplement LED changing patterns A and B using the Pin C++ class.
Generally the C++ class are split into two files.
- The declaration, referred to as the header file.
Pin.hwill indicate that the file declared the class Pin. Declaration is the process of defining what the class should do. - The implementation, referred to as the source file.
Pin.cppindicates that the file implement the declared functions and variables from “Pin.h”. Implementation is the process of writing the code, that determines how the declared functions are imlemented.
Pin.h file:
#ifndef PIN_H
#define PIN_H
#include <Arduino.h>
// This is a C++ class for an Arduino digital pin
class Pin {
public:
enum class Direction { OUT=0, IN=1, IN_PULLUP=2 };
// a class constructor with parameters
Pin( int8_t pin, Direction dir=Direction::IN, bool init_value=false );
// read the input pin
bool read( bool force_update=true );
// write the output pin
void write( bool value, bool force_update=true );
// toggle the output pin
void toggle( bool force_update=true ) ;
// assign a new value to the output pin
void operator=(bool value);
// set the direction of the pin
void setDirection( Direction dir, bool init_value=false );
// inline methods
inline operator bool() { return _value; }
inline int8_t getPin() { return _pin; }
inline bool getValue() { return _value; }
inline Direction getDirection() { return _dir; }
// the class destructor
~Pin() {}
protected:
// initialize the GPIO pin
void init( int8_t pin, Direction dir, bool init_value );
// update the logic state of the GPIO pin
void update();
private:
int8_t _pin; // the GPIO pin number
bool _value; // the value of pin
Direction _dir; // the direction of pin
};
#endif
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Pin.cpp file:
#include "Pin.h"
// Class implementation for Pin.h
Pin::Pin( int8_t pin, Direction dir, bool init_value ) {
init( pin, dir, init_value );
}
bool Pin::read( bool force_update ) {
if (force_update) { update(); }
return _value;
}
void Pin::write( bool value, bool force_update ) {
_value = value;
if (force_update) { update(); }
}
void Pin::toggle( bool force_update ) {
if ( _dir == Direction::OUT ) {
_value = !_value;
}
if (force_update) {
update();
}
}
void Pin::operator=(bool value) {
write( value );
}
void Pin::setDirection( Direction dir, bool init_value ) {
init( _pin, dir, init_value );
}
void Pin::init( int8_t pin, Direction dir, bool init_value ) {
_pin = pin;
_dir = dir;
_value = init_value;
if ( _dir == Direction::OUT ) {
pinMode( _pin, OUTPUT );
}
else if ( _dir == Direction::IN ) {
pinMode( _pin, INPUT );
}
else if ( _dir == Direction::IN_PULLUP ) {
pinMode( _pin, INPUT_PULLUP );
}
update();
}
void Pin::update() {
if ( _dir == Direction::OUT ) {
digitalWrite( _pin, _value ? true : false ) ;
//Serial.printf( "Debug> write output: %d on pin %d\n", _value, _pin );
}
else {
_value = digitalRead( _pin ) ? true : false;
//Serial.printf( "Debug> read input: %d on pin %d\n", _value, _pin );
}
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
LED changing pattern: A
- Step 1. Initially, only one LED (at index=0) is ON, and the rest of the LEDs are OFF.
- Step 2. The position of the ON LED should be moved to the next in a circular manner in a fixed time interval and then repeat Step 2.
Code:
#include "Pin.h"
#define DEFAULT_PIN (22) // (onboard LED)
#define OFF (0)
#define ON (1)
#define DELAY_MS (200)
// function prototypes
void blink(int);
int LED_PINS[] = {23, 22, 32, 33, 25, 26, 27, 14, 12, 13};
int num_pins = sizeof(LED_PINS) / sizeof(int);
void setup() {
//empty
}
void loop() {
for ( int i = 0; i < num_pins; i++ ) {
blink(LED_PINS[i]);
}
}
void blink( int led_pin = DEFAULT_PIN ) {
Pin pin(led_pin, Pin::Direction::OUT, OFF);
pin = ON;
delay(DELAY_MS);
pin = OFF;
delay(DELAY_MS);
}

Wokwi Simulator for this pattern: https://wokwi.com/projects/343940655127462484
LED changing pattern: B
- Step 1. Initially, all LEDs are OFF.
- Step 2. Turn on the LEDs one by one with a time delay, starting at index=0 until all LEDs are ON.
- Step 3. If all LEDs are ON, turn off LEDs one by one starting at index=n-1, where n is the total number of LEDs, until all LEDs are OFF, and repeat Steps 2-3.
Code:
#include "Pin.h"
#define DEFAULT_PIN (22) // (onboard LED)
#define OFF (0)
#define ON (1)
#define DELAY_MS (100)
// function prototypes
void turn_led_on(int);
void turn_led_off(int);
int LED_PINS[] = {23, 22, 32, 33, 25, 26, 27, 14, 12, 13};
int num_pins = sizeof(LED_PINS) / sizeof(int);
void setup() {
//empty
}
void loop() {
for ( int i = 0; i < num_pins; i++ ) {
turn_led_on(LED_PINS[i]);
}
for ( int i = 0; i < num_pins; i++ ) {
turn_led_off(LED_PINS[num_pins-1-i]);
}
}
void turn_led_on( int led_pin = DEFAULT_PIN ) {
Pin pin(led_pin, Pin::Direction::OUT, ON);
delay(DELAY_MS);
}
void turn_led_off( int led_pin = DEFAULT_PIN ) {
Pin pin(led_pin, Pin::Direction::OUT, OFF);
delay(DELAY_MS);
}

Wokwi Simulator for this pattern: https://wokwi.com/projects/343949402636812884